Karampatsas, K; Hall, T; Voysey, M; Carreras-Abad, C; Cochet, M; Ramkhelawon, L; Peregrine, E; Andrews, N; Heath, PT; Le Doare, K
(2024)
Antibody kinetics between birth and three months of life in healthy infants with natural exposure to Group B streptococcus: A UK cohort study.
Vaccine, 42 (13).
pp. 3230-3238.
ISSN 0264-410X
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2024.04.014
SGUL Authors: Le Doare, Kirsty Karampatsas, Konstantinos Heath, Paul Trafford
|
PDF
Published Version
Available under License Creative Commons Attribution. Download (1MB) | Preview |
|
|
Microsoft Word (.docx)
Accepted Version
Available under License Creative Commons Attribution. Download (353kB) |
||
|
Microsoft PowerPoint (Fig 1)
Accepted Version
Available under License Creative Commons Attribution. Download (41kB) |
||
![[img]](https://openaccess.sgul.ac.uk/116411/4.hassmallThumbnailVersion/Fig%202.png)
|
Image (PNG) (Fig 2)
Accepted Version
Available under License ["licenses_description_publisher" not defined]. Download (901kB) | Preview |
|
![[img]](https://openaccess.sgul.ac.uk/116411/9.hassmallThumbnailVersion/Fig%203.png)
|
Image (PNG) (Fig 3)
Accepted Version
Available under License Creative Commons Attribution. Download (1MB) | Preview |
|
![[img]](https://openaccess.sgul.ac.uk/116411/18.hassmallThumbnailVersion/Fig%204.png)
|
Image (PNG) (Fig 4)
Accepted Version
Available under License Creative Commons Attribution. Download (30kB) | Preview |
|
![[img]](https://openaccess.sgul.ac.uk/116411/23.hassmallThumbnailVersion/Fig%205.png)
|
Image (PNG) (Fig 5)
Accepted Version
Available under License Creative Commons Attribution. Download (909kB) | Preview |
|
![[img]](https://openaccess.sgul.ac.uk/116411/28.hassmallThumbnailVersion/Fig%20S1.png)
|
Image (PNG) (Fig S1)
Supplemental Material
Download (37kB) | Preview |
Abstract
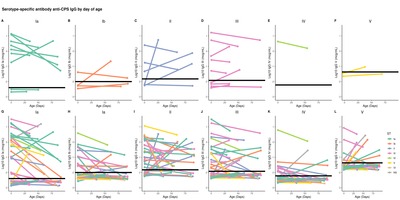
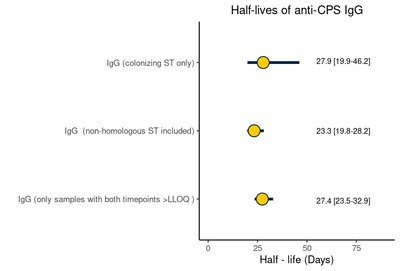
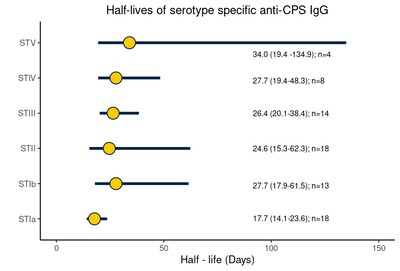
Introduction Capsular polysaccharide (CPS) serotype-specific Immunoglobulin G (IgG) in cord blood has been proposed as a correlate of protection against invasive Group B Streptococcus (iGBS) disease. Although protective levels are required in infants throughout the window of vulnerability up to 3 months of age, little is known regarding the kinetics of GBS-specific IgG over this period. Methods We enrolled 33 healthy infants born to mothers colonized with GBS. We collected cord blood and infant blood samples either at one (21–35 days), two (49–63 days), or three months of age (77–91 days). We measured GBS serotype-specific CPS IgG concentrations and calculated the decay rate using a mixed-effects model. We further explored whether the antibody kinetics were affected by common maternal and infant factors and estimated the correlation between IgG concentration at birth and one, two, and three months of age. Results The half-life estimate of IgG concentration for homologous and non-homologous GBS serotypes in paired samples with detectable IgG levels at both time points was 27.4 (95 % CI: 23.5–32.9) days. The decay rate did not vary by maternal age (p = 0.7), ethnicity (p = 0.1), gravida (p = 0.1), gestation (p = 0.7), and infant sex (p = 0.1). Predicted IgG titres above the assay lower limit of quantification on day 30 strongly correlated with titres at birth (Spearman correlation coefficient 0.71 [95 % CI: 0.60–0.80]). Conclusion Our results provide a basis for future investigations into the use of antibody kinetics in defining a serocorrelate of protection against late-onset iGBS disease.
| Item Type: | Article | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Additional Information: | © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd. This is an open access article under the CC BY license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/). | |||||||||
| Keywords: | 06 Biological Sciences, 07 Agricultural and Veterinary Sciences, 11 Medical and Health Sciences, Virology | |||||||||
| SGUL Research Institute / Research Centre: | Academic Structure > Infection and Immunity Research Institute (INII) | |||||||||
| Journal or Publication Title: | Vaccine | |||||||||
| ISSN: | 0264-410X | |||||||||
| Publisher License: | Creative Commons: Attribution 4.0 | |||||||||
| Projects: |
|
|||||||||
| Dates: |
|
|||||||||
| URI: | https://openaccess.sgul.ac.uk/id/eprint/116411 | |||||||||
| Publisher's version: | https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2024.04.014 |
Statistics
Actions (login required)
 |
Edit Item |