Zivanovic, N;
Öner, D;
Abraham, Y;
McGinley, J;
Drysdale, SB;
Wildenbeest, JG;
Crabbe, M;
Vanhoof, G;
Thys, K;
Thwaites, RS;
et al.
Zivanovic, N; Öner, D; Abraham, Y; McGinley, J; Drysdale, SB; Wildenbeest, JG; Crabbe, M; Vanhoof, G; Thys, K; Thwaites, RS; Robinson, H; Bont, L; Openshaw, PJM; Martinón-Torres, F; RESCEU Investigators; Pollard, AJ; Aerssens, J
(2023)
Single-cell immune profiling reveals markers of emergency myelopoiesis that distinguish severe from mild respiratory syncytial virus disease in infants.
Clin Transl Med, 13 (12).
e1507.
ISSN 2001-1326
https://doi.org/10.1002/ctm2.1507
SGUL Authors: Drysdale, Simon Bruce
|
PDF
Published Version
Available under License Creative Commons Attribution. Download (3MB) | Preview |
|
|
Microsoft Word (.docx) (Supplementary material)
Published Version
Available under License Creative Commons Attribution. Download (30kB) |
||
![[img]](https://openaccess.sgul.ac.uk/115932/8.hassmallThumbnailVersion/ctm21507-sup-0002-figures1.jpeg)
|
Image (JPEG) (Figure S1)
Published Version
Available under License Creative Commons Attribution. Download (191kB) | Preview |
|
|
Image (TIFF) (Figure S2)
Published Version
Available under License Creative Commons Attribution. Download (3MB) | Preview |
|
|
Image (TIFF) (Figure S3)
Published Version
Available under License Creative Commons Attribution. Download (1MB) | Preview |
|
|
Image (TIFF) (Figure S4)
Published Version
Available under License Creative Commons Attribution. Download (794kB) | Preview |
|
|
Image (TIFF) (Figure S5)
Published Version
Available under License Creative Commons Attribution. Download (1MB) | Preview |
|
![[img]](https://openaccess.sgul.ac.uk/115932/37.hassmallThumbnailVersion/ctm21507-sup-0007-figures6.jpg)
|
Image (JPEG) (Figure S6)
Published Version
Available under License Creative Commons Attribution. Download (250kB) | Preview |
|
|
Image (TIFF) (Figure S7)
Published Version
Available under License Creative Commons Attribution. Download (1MB) | Preview |
|
![[img]](https://openaccess.sgul.ac.uk/115932/49.hassmallThumbnailVersion/ctm21507-sup-0009-figures8.png)
|
Image (PNG) (Figure S8)
Published Version
Available under License Creative Commons Attribution. Download (151kB) | Preview |
Abstract
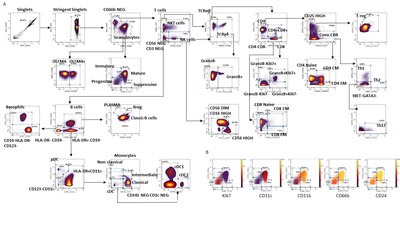
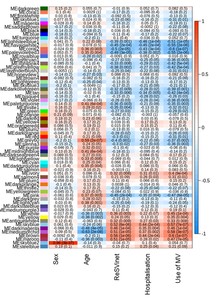
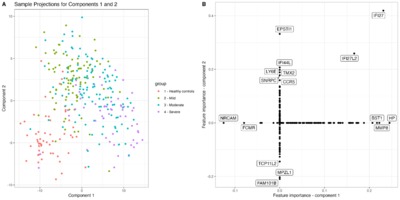
Whereas most infants infected with respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) show no or only mild symptoms, an estimated 3 million children under five are hospitalized annually due to RSV disease. This study aimed to investigate biological mechanisms and associated biomarkers underlying RSV disease heterogeneity in young infants, enabling the potential to objectively categorize RSV-infected infants according to their medical needs. Immunophenotypic and functional profiling demonstrated the emergence of immature and progenitor-like neutrophils, proliferative monocytes (HLA-DRLow , Ki67+), impaired antigen-presenting function, downregulation of T cell response and low abundance of HLA-DRLow B cells in severe RSV disease. HLA-DRLow monocytes were found as a hallmark of RSV-infected infants requiring hospitalization. Complementary transcriptomics identified genes associated with disease severity and pointed to the emergency myelopoiesis response. These results shed new light on mechanisms underlying the pathogenesis and development of severe RSV disease and identified potential new candidate biomarkers for patient stratification.
| Item Type: | Article | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Additional Information: | © 2023 The Authors. Clinical and Translational Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Shanghai Institute of Clinical Bioinformatics. This is an open access article under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. | ||||||||
| Keywords: | 1110 Nursing | ||||||||
| SGUL Research Institute / Research Centre: | Academic Structure > Infection and Immunity Research Institute (INII) | ||||||||
| Journal or Publication Title: | Clin Transl Med | ||||||||
| ISSN: | 2001-1326 | ||||||||
| Language: | eng | ||||||||
| Publisher License: | Creative Commons: Attribution 4.0 | ||||||||
| Projects: |
|
||||||||
| PubMed ID: | 38115705 | ||||||||
| Dates: |
|
||||||||
 |
Go to PubMed abstract | ||||||||
| URI: | https://openaccess.sgul.ac.uk/id/eprint/115932 | ||||||||
| Publisher's version: | https://doi.org/10.1002/ctm2.1507 |
Statistics
Actions (login required)
 |
Edit Item |