Minopoli, M; Noël, L; Meroni, A; Mascherpa, M; Frick, A; Thilaganathan, B
(2023)
Adverse pregnancy outcomes in women at increased risk of preterm pre-eclampsia on first-trimester combined screening.
BJOG, 131 (1).
pp. 81-87.
ISSN 1471-0528
https://doi.org/10.1111/1471-0528.17560
SGUL Authors: Thilaganathan, Baskaran
|
PDF
Published Version
Available under License Creative Commons Attribution. Download (401kB) | Preview |
|
![[img]](https://openaccess.sgul.ac.uk/115539/6.hassmallThumbnailVersion/bjo17560-sup-0001-figures1.jpg)
|
Image (JPEG) (Figure S1)
Published Version
Available under License Creative Commons Attribution. Download (912kB) | Preview |
|
![[img]](https://openaccess.sgul.ac.uk/115539/11.hassmallThumbnailVersion/bjo17560-sup-0002-figures2.jpg)
|
Image (JPEG) (Figure S2)
Published Version
Available under License Creative Commons Attribution. Download (760kB) | Preview |
|
![[img]](https://openaccess.sgul.ac.uk/115539/16.hassmallThumbnailVersion/bjo17560-sup-0003-figures3.jpg)
|
Image (JPEG) (Figure S3)
Published Version
Available under License Creative Commons Attribution. Download (776kB) | Preview |
|
|
Microsoft Word (.docx) (Tables S1–S4)
Published Version
Available under License Creative Commons Attribution. Download (30kB) |
Abstract
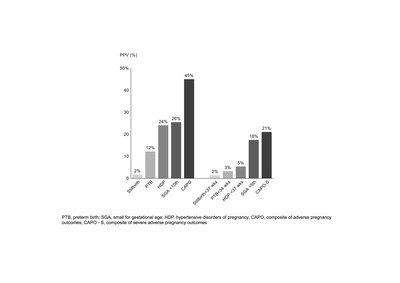
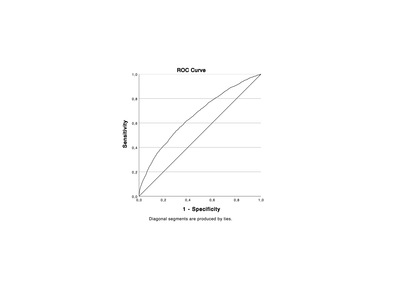
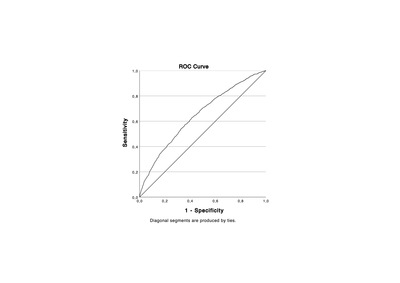
OBJECTIVE: Uteroplacental dysfunction may not only result in pre-eclampsia (PE) but also in preterm birth (PTB), small-for-gestational-age (SGA) birth and stillbirth. The aim of this study is to evaluate the positive predictive value (PPV) of first-trimester combined PE screening for all of these placenta-mediated adverse pregnancy outcomes. DESIGN: Retrospective cohort study. SETTING: Tertiary referral maternity unit. SAMPLE: A total of 13 211 singleton pregnancies. METHODS: First-trimester combined screening for preterm PE using the Fetal Medicine Foundation (FMF) algorithm. MAIN OUTCOMES MEASURES: Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (HDP), PTB, SGA birth and stillbirth were combined to assess composite adverse and severe adverse pregnancy outcomes (CAPO and CAPO-S). The PPVs for CAPO and CAPO-S were calculated for women with a combined risk for preterm PE of ≥1 in 50 and ≥1 in 100. RESULTS: First-trimester combined screening identified 2215 women (16.8%) with a risk of ≥1 in 100 for preterm PE. The PPVs for a risk of ≥1 in 100 for CAPO and CAPO-S were 38.8% and 18.2%, respectively. The equivalent PPVs for a risk of ≥1 in 50 were 45.1% and 21.1%, respectively. CONCLUSIONS: Women identified at high risk of preterm PE are also at increased risk of other placenta-mediated adverse pregnancy outcomes, such as PTB, SGA birth and stillbirth. Women at high risk for preterm PE after first-trimester screening may benefit from a higher surveillance care pathway, with interventions to mitigate all the adverse outcomes associated with placental dysfunction.
| Item Type: | Article | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Additional Information: | © 2023 The Authors. BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd. This is an open access article under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. | ||||||||
| Keywords: | composite adverse outcomes of pregnancy, first trimester, pre-eclampsia, preterm birth, screening, small for gestational age, stillbirth, uteroplacental dysfunction, composite adverse outcomes of pregnancy, first trimester, pre-eclampsia, preterm birth, screening, small for gestational age, stillbirth, uteroplacental dysfunction, 11 Medical and Health Sciences, Obstetrics & Reproductive Medicine | ||||||||
| SGUL Research Institute / Research Centre: | Academic Structure > Molecular and Clinical Sciences Research Institute (MCS) | ||||||||
| Journal or Publication Title: | BJOG | ||||||||
| ISSN: | 1471-0528 | ||||||||
| Language: | eng | ||||||||
| Publisher License: | Creative Commons: Attribution 4.0 | ||||||||
| PubMed ID: | 37271740 | ||||||||
| Web of Science ID: | WOS:001000684200001 | ||||||||
| Dates: |
|
||||||||
 |
Go to PubMed abstract | ||||||||
| URI: | https://openaccess.sgul.ac.uk/id/eprint/115539 | ||||||||
| Publisher's version: | https://doi.org/10.1111/1471-0528.17560 |
Statistics
Actions (login required)
 |
Edit Item |