Wiseman, DJ; Thwaites, RS; Drysdale, SB; Janet, S; Donaldson, GC; Wedzicha, JA; Openshaw, PJ; RESCEU Investigators
(2020)
Immunological and Inflammatory Biomarkers of Susceptibility and Severity in Adult Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infections.
J Infect Dis, 222 (Supplement 7).
S584-S591.
ISSN 1537-6613
https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jiaa063
SGUL Authors: Drysdale, Simon Bruce
|
Microsoft Word (.doc)
Accepted Version
Available under License ["licenses_description_publisher" not defined]. Download (142kB) |
||
![[img]](https://openaccess.sgul.ac.uk/111839/3.hassmallThumbnailVersion/Figure_1_Wiseman.png)
|
Image (PNG) (Figure 1)
Accepted Version
Available under License ["licenses_description_publisher" not defined]. Download (21kB) | Preview |
|
|
Microsoft Word (.docx) (Tables)
Accepted Version
Available under License ["licenses_description_publisher" not defined]. Download (23kB) |
Abstract
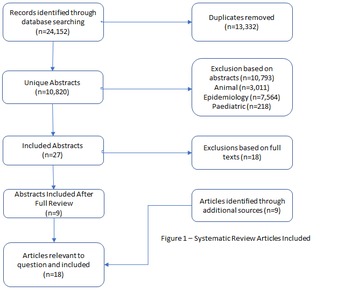
BACKGROUND: . Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is the most common cause of bronchiolitis in young infants. However, it is also a significant pathogen in older adults. Validated biomarkers of RSV disease severity would benefit diagnostics, treatment decisions, and prophylactic interventions. This review summarizes knowledge of biomarkers for RSV disease in adults. METHODS: A literature review was performed using Ovid Medline, Embase, Global health, Scopus, and Web of Science for articles published 1946-October 2016. Nine articles were identified plus 9 from other sources. RESULTS: From observational studies of natural infection and challenge studies in volunteers, biomarkers of RSV susceptibility or disease severity in adults were: (1) lower anti-RSV neutralizing antibodies, where neutralizing antibody (and local IgA) may be a correlate of susceptibility/severity; (2) RSV-specific CD8+ T cells in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid preinfection (subjects with higher levels had less severe illness); and (3) elevated interleukin-6 (IL-6), IL-8, and myeloperoxidase levels in the airway are indicative of severe infection. CONCLUSIONS: Factors determining susceptibility to and severity of RSV disease in adults have not been well defined. Respiratory mucosal antibodies and CD8+ T cells appear to contribute to preventing infection and modulation of disease severity. Studies of RSV pathogenesis in at-risk populations are needed.
| Item Type: | Article | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Additional Information: | This is a pre-copyedited, author-produced version of an article accepted for publication in The Journal of Infectious Diseases following peer review. The version of record Dexter J Wiseman, Ryan S Thwaites, Simon B Drysdale, Sophie Janet, Gavin C Donaldson, Jadwiga A Wedzicha, Peter J Openshaw, RESCEU Investigators, Immunological and Inflammatory Biomarkers of Susceptibility and Severity in Adult Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infections, The Journal of Infectious Diseases, Volume 222, Issue Supplement_7, 1 November 2020, Pages S584–S591 is available online at: https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jiaa063 | ||||
| Keywords: | COPD, IL-6, MPO, RESCEU, RSV, adult, biomarker, neutralizing antibody, respiratory syncytial virus, severity, RESCEU Investigators, 11 Medical and Health Sciences, 06 Biological Sciences, Microbiology | ||||
| SGUL Research Institute / Research Centre: | Academic Structure > Infection and Immunity Research Institute (INII) | ||||
| Journal or Publication Title: | J Infect Dis | ||||
| ISSN: | 1537-6613 | ||||
| Language: | eng | ||||
| Publisher License: | Publisher's own licence | ||||
| PubMed ID: | 32227102 | ||||
| Dates: |
|
||||
 |
Go to PubMed abstract | ||||
| URI: | https://openaccess.sgul.ac.uk/id/eprint/111839 | ||||
| Publisher's version: | https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jiaa063 |
Statistics
Actions (login required)
 |
Edit Item |