Öner, D; Drysdale, SB; McPherson, C; Lin, G-L; Janet, S; Broad, J; Pollard, AJ; Aerssens, J; RESCEU Investigators
(2020)
Biomarkers for Disease Severity in Children Infected With Respiratory Syncytial Virus: A Systematic Literature Review.
J Infect Dis, 222 (Supplement 7).
S648-S657.
ISSN 1537-6613
https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jiaa208
SGUL Authors: Drysdale, Simon Bruce
|
Microsoft Word (.docx)
Accepted Version
Available under License ["licenses_description_publisher" not defined]. Download (815kB) |
||
![[img]](https://openaccess.sgul.ac.uk/112320/6.hassmallThumbnailVersion/Figure1_v1%20PUBLISHED.png)
|
Image (PNG) (Figure 1)
Accepted Version
Available under License ["licenses_description_publisher" not defined]. Download (618kB) | Preview |
|
|
Microsoft Word (.docx) (Supplementary information)
Accepted Version
Available under License ["licenses_description_publisher" not defined]. Download (496kB) |
Abstract
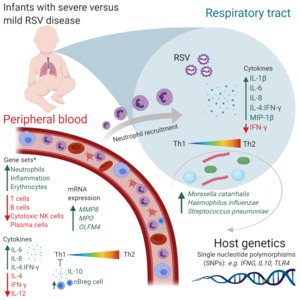
BACKGROUND: Clinical manifestations of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infection vary widely from mild, self-limiting illness to severe life-threatening disease. There are gaps in knowledge of biomarkers to objectively define severe disease and predict clinical outcomes. METHODS: A systematic search was performed, 1945-March 2019 in databases Ovid Medline, Embase, Global health, Scopus, and Web of Science. Risk of bias was assessed using the Cochrane tool. RESULTS: A total of 25 132 abstracts were screened and studies were assessed for quality, risk of bias, and extracted data; 111 studies met the inclusion criteria. RSV severity was correlated with antibody titers, reduced T and B cells, dysregulated innate immunity, neutrophil mobilization to the lungs and blood, decreased Th1 response, and Th2 weighted shift. Microbial exposures in respiratory tract may contribute to neutrophil mobilization to the lungs of the infants with severe RSV compared with mild RSV disease. CONCLUSIONS: Although a wide range of biomarkers have been associated with RSV disease severity, robust validated biomarkers are lacking. This review illustrates the broad heterogeneity of study designs and high variability in the definition of severe RSV disease. Prospective studies are required to validate biomarkers. Additional research investigating epigenetics, metabolomics, and microbiome holds promise for novel biomarkers.
| Item Type: | Article | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Additional Information: | This is a pre-copyedited, author-produced version of an article accepted for publication in the Journal of Infectious Diseases following peer review. The version of record Deniz Öner, Simon B Drysdale, Calum McPherson, Gu-Lung Lin, Sophie Janet, Jonathan Broad, Andrew J Pollard, Jeroen Aerssens, RESCEU Investigators, Biomarkers for Disease Severity in Children Infected With Respiratory Syncytial Virus: A Systematic Literature Review, The Journal of Infectious Diseases, Volume 222, Issue Supplement_7, 1 November 2020, Pages S648–S657 is available online at: https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jiaa208 | ||||||||
| Keywords: | biomarkers, bronchiolitis, infant, lower respiratory tract infection (LRTI), respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), severe RSV disease, RESCEU Investigators, biomarkers, bronchiolitis, infant, lower respiratory tract infection (LRTI), respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), severe RSV disease, Microbiology, 11 Medical and Health Sciences, 06 Biological Sciences | ||||||||
| SGUL Research Institute / Research Centre: | Academic Structure > Infection and Immunity Research Institute (INII) | ||||||||
| Journal or Publication Title: | J Infect Dis | ||||||||
| ISSN: | 1537-6613 | ||||||||
| Language: | eng | ||||||||
| Dates: |
|
||||||||
| Publisher License: | Publisher's own licence | ||||||||
| Projects: |
|
||||||||
| PubMed ID: | 32794555 | ||||||||
 |
Go to PubMed abstract | ||||||||
| URI: | https://openaccess.sgul.ac.uk/id/eprint/112320 | ||||||||
| Publisher's version: | https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jiaa208 |
Statistics
Actions (login required)
 |
Edit Item |