Nightingale, CM; Donin, AS; Kerry, SR; Owen, CG; Rudnicka, AR; Brage, S; Westgate, KL; Ekelund, U; Cook, DG; Whincup, PH
(2016)
Cross-sectional study of ethnic differences in physical fitness among children of South Asian, black African-Caribbean and white European origin: the Child Heart and Health Study in England (CHASE).
BMJ Open, 6 (6).
ISSN 2044-6055
https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2016-011131
SGUL Authors: Cook, Derek Gordon Nightingale, Claire Owen, Christopher Grant Whincup, Peter Hynes Kerry-Barnard, Sarah Ruth Donin, Angela
|
Microsoft Word (.doc)
Accepted Version
Available under License Creative Commons Attribution. Download (107kB) |
||
|
Microsoft Word (.docx)
Accepted Version
Available under License Creative Commons Attribution. Download (21kB) |
||
![[img]](https://openaccess.sgul.ac.uk/107944/5.hassmallThumbnailVersion/Supplementary%20Figure%201.jpg)
|
Image (JPEG)
Accepted Version
Available under License Creative Commons Attribution. Download (381kB) | Preview |
|
|
PDF
Published Version
Available under License Creative Commons Attribution. Download (708kB) | Preview |
Abstract
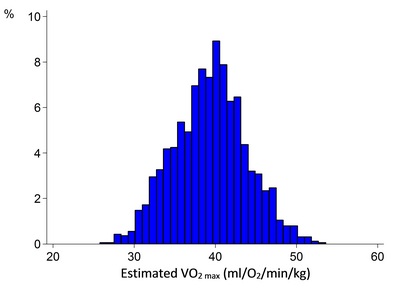
OBJECTIVE: Little is known about levels of physical fitness in children from different ethnic groups in the UK. We therefore studied physical fitness in UK children (aged 9-10 years) of South Asian, black African-Caribbean and white European origin. DESIGN: Cross-sectional study. SETTING: Primary schools in the UK. PARTICIPANTS: 1625 children (aged 9-10 years) of South Asian, black African-Caribbean and white European origin in the UK studied between 2006 and 2007. OUTCOME MEASURES: A step test assessed submaximal physical fitness from which estimated VO2 max was derived. Ethnic differences in estimated VO2 max were estimated using multilevel linear regression allowing for clustering at school level and adjusting for age, sex and month as fixed effects. RESULTS: The study response rate was 63%. In adjusted analyses, boys had higher levels of estimated VO2 max than girls (mean difference 3.06 mL O2/min/kg, 95% CI 2.66 to 3.47, p<0.0001). Levels of estimated VO2 max were lower in South Asians than those in white Europeans (mean difference -0.79 mL O2/min/kg, 95% CI -1.41 to -0.18, p=0.01); levels of estimated VO2 max in black African-Caribbeans were higher than those in white Europeans (mean difference 0.60 mL O2/min/kg, 95% CI 0.02 to 1.17, p=0.04); these patterns were similar in boys and girls. The lower estimated VO2 max in South Asians, compared to white Europeans, was consistent among Indian, Pakistani and Bangladeshi children and was attenuated by 78% after adjustment for objectively measured physical activity (average daily steps). CONCLUSIONS: South Asian children have lower levels of physical fitness than white Europeans and black African-Caribbeans in the UK. This ethnic difference in physical fitness is at least partly explained by ethnic differences in physical activity.
| Item Type: | Article | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Additional Information: | This is an Open Access article distributed in accordance with the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt and build upon this work, for commercial use, provided the original work is properly cited. See: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ | ||||||||||||
| Keywords: | Children, Ethnicity, Physical fitness | ||||||||||||
| SGUL Research Institute / Research Centre: | Academic Structure > Population Health Research Institute (INPH) | ||||||||||||
| Journal or Publication Title: | BMJ Open | ||||||||||||
| Article Number: | e011131 | ||||||||||||
| ISSN: | 2044-6055 | ||||||||||||
| Language: | eng | ||||||||||||
| Publisher License: | Creative Commons: Attribution 4.0 | ||||||||||||
| Projects: |
|
||||||||||||
| PubMed ID: | 27324713 | ||||||||||||
| Dates: |
|
||||||||||||
 |
Go to PubMed abstract | ||||||||||||
| URI: | https://openaccess.sgul.ac.uk/id/eprint/107944 | ||||||||||||
| Publisher's version: | https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2016-011131 |
Statistics
Actions (login required)
 |
Edit Item |