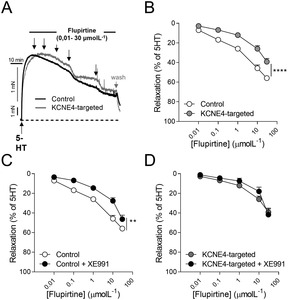
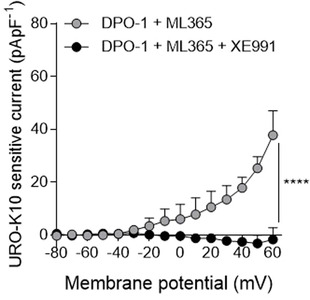
Villegas-Esguevillas, M;
Cho, S;
Vera-Zambrano, A;
Kwon, JW;
Barreira, B;
Telli, G;
Navarro-Dorado, J;
Morales-Cano, D;
de Olaiz, B;
Moreno, L;
et al.
Villegas-Esguevillas, M; Cho, S; Vera-Zambrano, A; Kwon, JW; Barreira, B; Telli, G; Navarro-Dorado, J; Morales-Cano, D; de Olaiz, B; Moreno, L; Greenwood, I; Pérez-Vizcaíno, F; Kim, SJ; Climent, B; Cogolludo, A
(2023)
The novel KV7 channel activator URO-K10 exerts enhanced pulmonary vascular effects independent of the KCNE4 regulatory subunit.
Biomed Pharmacother, 164.
p. 114952.
ISSN 1950-6007
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114952
SGUL Authors: Greenwood, Iain Andrew
|
PDF
Published Version
Available under License Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial No Derivatives. Download (5MB) | Preview |
|
![[img]](https://openaccess.sgul.ac.uk/115577/6.hassmallThumbnailVersion/1-s2.0-S0753332223007424-mmc1_lrg.jpg)
|
Image (JPEG) (Supplementary Figure 1)
Published Version
Available under License Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial No Derivatives. Download (339kB) | Preview |
|
![[img]](https://openaccess.sgul.ac.uk/115577/11.hassmallThumbnailVersion/1-s2.0-S0753332223007424-mmc2_lrg.jpg)
|
Image (JPEG) (Supplementary Figure 2)
Published Version
Available under License Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial No Derivatives. Download (404kB) | Preview |
|
![[img]](https://openaccess.sgul.ac.uk/115577/16.hassmallThumbnailVersion/1-s2.0-S0753332223007424-mmc3_lrg.jpg)
|
Image (JPEG) (Supplementary Figure 3)
Published Version
Available under License Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial No Derivatives. Download (384kB) | Preview |
|
![[img]](https://openaccess.sgul.ac.uk/115577/21.hassmallThumbnailVersion/1-s2.0-S0753332223007424-mmc4_lrg.jpg)
|
Image (JPEG) (Supplementary Figure 4)
Published Version
Available under License Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial No Derivatives. Download (265kB) | Preview |
|
![[img]](https://openaccess.sgul.ac.uk/115577/26.hassmallThumbnailVersion/1-s2.0-S0753332223007424-mmc5_lrg.jpg)
|
Image (JPEG) (Supplementary Figure 5)
Published Version
Available under License Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial No Derivatives. Download (264kB) | Preview |
|
![[img]](https://openaccess.sgul.ac.uk/115577/31.hassmallThumbnailVersion/1-s2.0-S0753332223007424-mmc6_lrg.jpg)
|
Image (JPEG) (Supplementary Figure 6)
Published Version
Available under License Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial No Derivatives. Download (174kB) | Preview |
|
![[img]](https://openaccess.sgul.ac.uk/115577/40.hassmallThumbnailVersion/1-s2.0-S0753332223007424-mmc7_lrg.jpg)
|
Image (JPEG) (Supplementary Figure 7)
Published Version
Available under License Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial No Derivatives. Download (462kB) | Preview |
|
![[img]](https://openaccess.sgul.ac.uk/115577/45.hassmallThumbnailVersion/1-s2.0-S0753332223007424-mmc8_lrg.jpg)
|
Image (JPEG) (Supplementary Figure 8)
Published Version
Available under License Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial No Derivatives. Download (508kB) | Preview |
|
![[img]](https://openaccess.sgul.ac.uk/115577/50.hassmallThumbnailVersion/1-s2.0-S0753332223007424-mmc9_lrg.jpg)
|
Image (JPEG) (Supplementary Figure 9)
Published Version
Available under License Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial No Derivatives. Download (584kB) | Preview |
|
![[img]](https://openaccess.sgul.ac.uk/115577/55.hassmallThumbnailVersion/1-s2.0-S0753332223007424-mmc10_lrg.jpg)
|
Image (JPEG) (Supplementary Figure 10)
Published Version
Available under License Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial No Derivatives. Download (205kB) | Preview |
Abstract
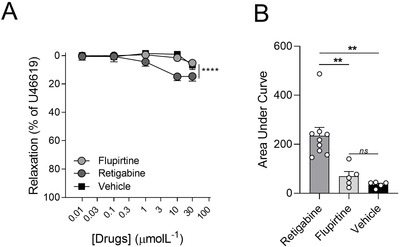
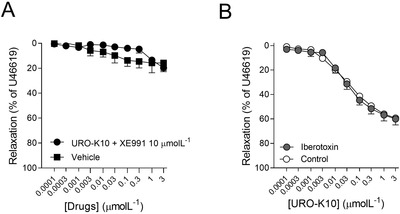
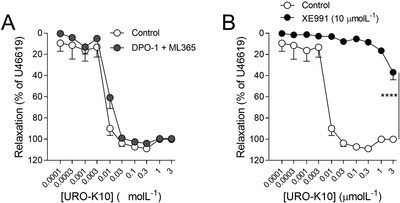
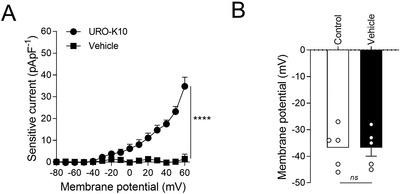
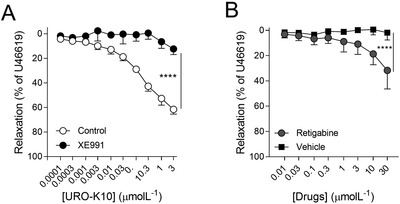
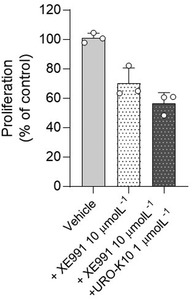
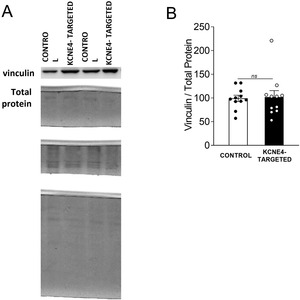
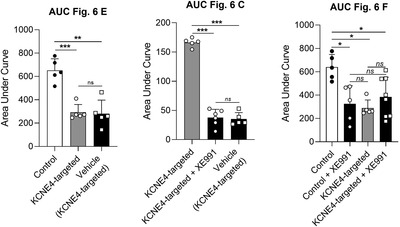
KV7 channels exert a pivotal role regulating vascular tone in several vascular beds. In this context, KV7 channel agonists represent an attractive strategy for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). Therefore, in this study, we have explored the pulmonary vascular effects of the novel KV7 channel agonist URO-K10. Consequently, the vasodilator and electrophysiological effects of URO-K10 were tested in rat and human pulmonary arteries (PA) and PA smooth muscle cells (PASMC) using myography and patch-clamp techniques. Protein expression was also determined by Western blot. Morpholino-induced knockdown of KCNE4 was assessed in isolated PA. PASMC proliferation was measured by BrdU incorporation assay. In summary, our data show that URO-K10 is a more effective relaxant of PA than the classical KV7 activators retigabine and flupirtine. URO-K10 enhanced KV currents in PASMC and its electrophysiological and relaxant effects were inhibited by the KV7 channel blocker XE991. The effects of URO-K10 were confirmed in human PA. URO-K10 also exhibited antiproliferative effects in human PASMC. Unlike retigabine and flupirtine, URO-K10-induced pulmonary vasodilation was not affected by morpholino-induced knockdown of the KCNE4 regulatory subunit. Noteworthy, the pulmonary vasodilator efficacy of this compound was considerably increased under conditions mimicking the ionic remodelling (as an in vitro model of PAH) and in PA from monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertensive rats. Taking all together, URO-K10 behaves as a KCNE4-independent KV7 channel activator with much increased pulmonary vascular effects compared to classical KV7 channel activators. Our study identifies a promising new drug in the context of PAH.
| Item Type: | Article | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Additional Information: | © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Masson SAS. This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/). | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Keywords: | K(V)7 channel activator, KCNE4 regulatory subunit, KCNQ, Potassium channels, Pulmonary hypertension, Vasodilation, Rats, Humans, Animals, KCNQ Potassium Channels, Morpholinos, Vasodilator Agents, Potassium Channels, Voltage-Gated, Animals, Humans, Rats, Potassium Channels, Voltage-Gated, Vasodilator Agents, KCNQ Potassium Channels, Morpholinos, KV7 channel activator, Pulmonary hypertension, Vasodilation, KCNQ, Potassium channels, KCNE4 regulatory subunit, 1115 Pharmacology and Pharmaceutical Sciences, Oncology & Carcinogenesis | |||||||||||||||||||||
| SGUL Research Institute / Research Centre: | Academic Structure > Molecular and Clinical Sciences Research Institute (MCS) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Journal or Publication Title: | Biomed Pharmacother | |||||||||||||||||||||
| ISSN: | 1950-6007 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Language: | eng | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Dates: |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Publisher License: | Creative Commons: Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 4.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Projects: |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| PubMed ID: | 37295249 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Web of Science ID: | WOS:001018952500001 | |||||||||||||||||||||
 |
Go to PubMed abstract | |||||||||||||||||||||
| URI: | https://openaccess.sgul.ac.uk/id/eprint/115577 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Publisher's version: | https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114952 |
Statistics
Actions (login required)
 |
Edit Item |