Merola, A;
Romagnolo, A;
Dwivedi, AK;
Padovani, A;
Berg, D;
Garcia-Ruiz, PJ;
Fabbri, M;
Artusi, CA;
Zibetti, M;
Lopiano, L;
et al.
Merola, A; Romagnolo, A; Dwivedi, AK; Padovani, A; Berg, D; Garcia-Ruiz, PJ; Fabbri, M; Artusi, CA; Zibetti, M; Lopiano, L; Pilotto, A; Bonacina, S; Morgante, F; Zeuner, K; Griewing, C; Schaeffer, E; Rodriguez-Porcel, F; Kauffman, M; Turcano, P; de Oliveira, LM; Palermo, G; Shanks, E; Del Sorbo, F; Bonvegna, S; Savica, R; Munhoz, RP; Ceravolo, R; Cilia, R; Espay, AJ
(2020)
Benign versus malignant Parkinson disease: the unexpected silver lining of motor complications.
J Neurol, 267 (10).
pp. 2949-2960.
ISSN 1432-1459
https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-020-09954-6
SGUL Authors: Morgante, Francesca
|
Microsoft Word (.docx)
Accepted Version
Available under License ["licenses_description_publisher" not defined]. Download (86kB) |
||
![[img]](https://openaccess.sgul.ac.uk/112011/3.hassmallThumbnailVersion/Figure%201.png)
|
Image (PNG) (Figure 1)
Accepted Version
Available under License ["licenses_description_publisher" not defined]. Download (24kB) | Preview |
|
![[img]](https://openaccess.sgul.ac.uk/112011/8.hassmallThumbnailVersion/Figure%202.png)
|
Image (PNG) (Figure 2)
Accepted Version
Available under License ["licenses_description_publisher" not defined]. Download (36kB) | Preview |
|
![[img]](https://openaccess.sgul.ac.uk/112011/13.hassmallThumbnailVersion/Figure%203.png)
|
Image (PNG) (Figure 3)
Accepted Version
Available under License ["licenses_description_publisher" not defined]. Download (117kB) | Preview |
Abstract
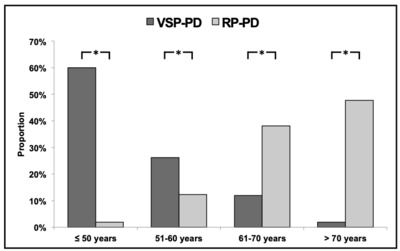
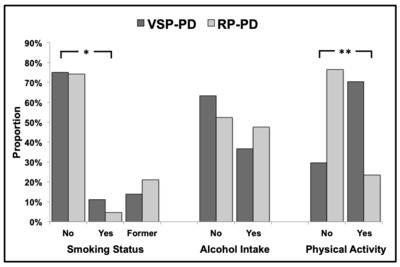
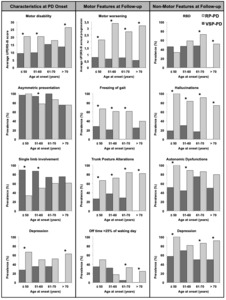
OBJECTIVE: We sought to evaluate demographic, clinical, and habits/occupational variables between phenotypic extremes in Parkinson's disease (PD). METHODS: Databases from nine movement disorders centers across seven countries were retrospectively searched for subjects meeting criteria for very slowly progressive, benign, PD (bPD) and rapidly progressive, malignant, PD (mPD). bPD was defined as Hoehn and Yahr (H&Y) stage ≤ 3, normal cognitive function, and Schwab and England (S&E) score ≥ 70 after ≥ 20 years of PD (≥ 10 years if older than 60 at PD onset); mPD as H&Y > 3, S&E score < 70, and cognitive impairment within 10 years from PD onset. We performed between-group analysis of demographic, habits/occupational, and clinical features at baseline and follow-up and unsupervised data-driven analysis of the clinical homogeneity of bPD and mPD. RESULTS: At onset, bPD subjects (n = 210) were younger, had a single limb affected, lower severity and greater asymmetry of symptoms, and lower prevalence of depression than mPD (n = 155). bPD was associated with active smoking and physical activity, mPD with agricultural occupation. At follow-up, mPD showed higher prevalence of depression, hallucinations, dysautonomia, and REM behaviour disorder. Interestingly, the odds of mPD were significantly reduced by the presence of dyskinesia and wearing-off. Data-driven analysis confirmed the independent clustering of bPD and mPD, with age at onset emerging as a critical discriminant between the two groups (< 46-year-old vs. > 68-year-old). CONCLUSIONS: Phenotypic PD extremes showed distinct demographic, clinical, and habits/occupational factors. Motor complications may be conceived as markers of therapeutic success given their attenuating effects on the odds of mPD.
| Item Type: | Article | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Additional Information: | This is a post-peer-review, pre-copyedit version of an article published in Journal of Neurology. The final authenticated version is available online at: http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00415-020-09954-6 | ||||||||
| Keywords: | Aging, Benign, Epidemiology, Malignant, Motor complications, Parkinson, Neurology & Neurosurgery, 1103 Clinical Sciences, 1109 Neurosciences | ||||||||
| SGUL Research Institute / Research Centre: | Academic Structure > Molecular and Clinical Sciences Research Institute (MCS) | ||||||||
| Journal or Publication Title: | J Neurol | ||||||||
| ISSN: | 1432-1459 | ||||||||
| Language: | eng | ||||||||
| Dates: |
|
||||||||
| Publisher License: | Publisher's own licence | ||||||||
| PubMed ID: | 32488298 | ||||||||
 |
Go to PubMed abstract | ||||||||
| URI: | https://openaccess.sgul.ac.uk/id/eprint/112011 | ||||||||
| Publisher's version: | https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-020-09954-6 |
Statistics
Actions (login required)
 |
Edit Item |